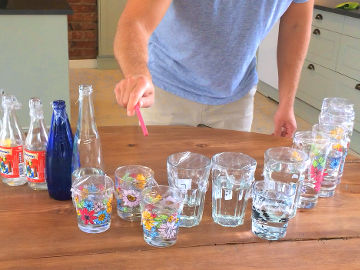Fun and easy science experiments for kids and adults.
Biology
Grow and shrink gummy bears by placing them in water with or without sugar. An experiment about how osmosis affects the cells.
| Gilla: | Dela: | |
Video

Materials
- 3 gummy bears
- 2 drinking glasses
- 1 spoon
- Sugar
- Refrigerator
- Something to heat water with (for example a microwave oven or a kettle)
Step 1

Step 2


Step 3


Step 4


Step 5


Step 6


Short explanation
In this demonstration, a gummy bear acts just like a cell. When it is surrounded by pure water, it absorbs water and swells, but when it surrounded by water with a lot of solutes in it, it gives off water and shrinks.Long explanation
A cell is bounded by and held together by its cell membrane, a thin membrane only a few molecules thick. Inside the cell membrane is the cell's entire contents, which are mostly water with solutes. The cell membrane is not completely impermeable. It is permeable to some substances, such as water. What determines whether water will migrate out or in through the cell membrane is how full the surrounding water is of other chemical substances. If a cell is surrounded by pure water, water migrates into the cell and it swells. If a cell is surrounded by, for example, salt water or sugar water, water migrates out of the cell and it shrinks. It is important to note that the chemical substances that are dissolved in the water cannot travel through the cell membrane. What determines which direction the water will travel is whether the water outside the cell contains more or less solutes than the water inside the cell. If the water inside and outside the cell contains the same amount of solutes, equilibrium has been reached and the cell no longer swells or shrinks. This process, when water travels through a membrane that lets water through but not the chemical substances that are dissolved in the water, is called osmosis. In fact, it doesn't matter what the solutes are. In this experiment, you used sugar, but you might as well have used salt. Osmosis is the reason you become dehydrated if you drink salt water. Your cells will then bathe in water that is full of solutes (salt) and water will migrate out of them. The cells shrink and will lack water. A gummy bear, or other gummy candy, consists mainly of gelatin. Then there's some water in them, as well as sugar and other additives. The gummy bear can, from an osmotic point of view, be seen as water with a whole lot of solutes in it. The reason why you have to heat water to dissolve sugar in it, is that this makes it a lot faster. This is because the water molecules move faster at high temperature.Experiment
This is actually already an experiment, but you can keep experimenting. This will make it a better science project. To do that, try answering one of the following questions. The answer to the question will be your hypothesis. Then test the hypothesis by doing the experiment.- How big will a gummy bear be after 1, 2, 4, 6, 12, 24, 48, 72 hours in water?
- Does it matter if you cover the glass or not?
- Is it possible to shrink a swollen gummy bear completely down to its former size again?
- What other things swell in water?
- What other things shrink in sugar water?
Variations


From its natural state, a potato cube can be made to both swell and shrink. However, it's difficult to get a gummy candy to shrink from its normal state. To succeed with this, you need to dissolve more sugar (or something else) in the water, than there is gelatin and other dissolved chemical substances in the gummy candy. It's possible, but the difference is hardly noticeable. So the benefits of using potato cubes are that you work with real cells and that you can both shrink and grow them. The downside is that the difference is not as big as with gummy candies. Also try other things that consist of cells. Berries or rice, for example, will give you a noticeable difference.
| Gilla: | Dela: | |
Similar
Latest
Content of website
© The Experiment Archive. Fun and easy science experiments for kids and adults. In biology, chemistry, physics, earth science, astronomy, technology, fire, air and water. To do in preschool, school, after school and at home. Also science fair projects and a teacher's guide.
To the top
© The Experiment Archive. Fun and easy science experiments for kids and adults. In biology, chemistry, physics, earth science, astronomy, technology, fire, air and water. To do in preschool, school, after school and at home. Also science fair projects and a teacher's guide.
To the top